Developing a Biodiversity Monitoring Framework for Aurora Sustainable Lands
Vision Statement - Aurora’s commitment to nature-based climate solutions
Aurora Sustainable Lands is a U.S.-based carbon stewardship company, specialising in carbon reduction strategies through nature-based climate solutions. The company provides carbon credits derived from improved forest management (IFM).
Aurora manages a substantial forest footprint across North America, spanning fourteen states and approximately 1.7 million acres. The company’s goal is to transform industrially harvested forests into carbon stewardship assets, generating high-quality carbon credits by implementing IFM practices that conserve forests, maximise carbon storage, and foster positive biodiversity outcomes.
To date, Aurora’s work has enhanced forest management practices across North America, primarily by increasing carbon storage and sequestration through climate-smart forestry methods such as deferred or reduced harvesting, extended-age rotation cycles, natural regeneration, and designated reserves or areas of high conservation value.
As biodiversity and nature have gained prominence on the global agenda, Aurora has become increasingly aware of the positive impacts its improved forest management regimes are having on biodiversity, including the protection of key habitats and species.
Project purpose – Monitoring and evaluating biodiversity interactions in Forest Management
Aurora is committed to understanding the biodiversity impact of its forestry practices. The goal is to monitor and report on biodiversity across its sites to support nature-based climate solutions strategy.
Challenge – Developing a science-driven framework for monitoring and insights
Aurora aims to improve its understanding of the interactions between forest management interventions and biodiversity, and to explore options for monitoring and reporting biodiversity at Aurora sites. Aurora staff required scientific guidance and strategic advice to identify key biodiversity indicators and monitoring methods that they could use to establish baseline conditions and assess the impact of their interventions across project sites. Aurora aimed to establish a science-driven framework to generate actionable insights.
Our approach – Translating data into actionable biodiversity indicators
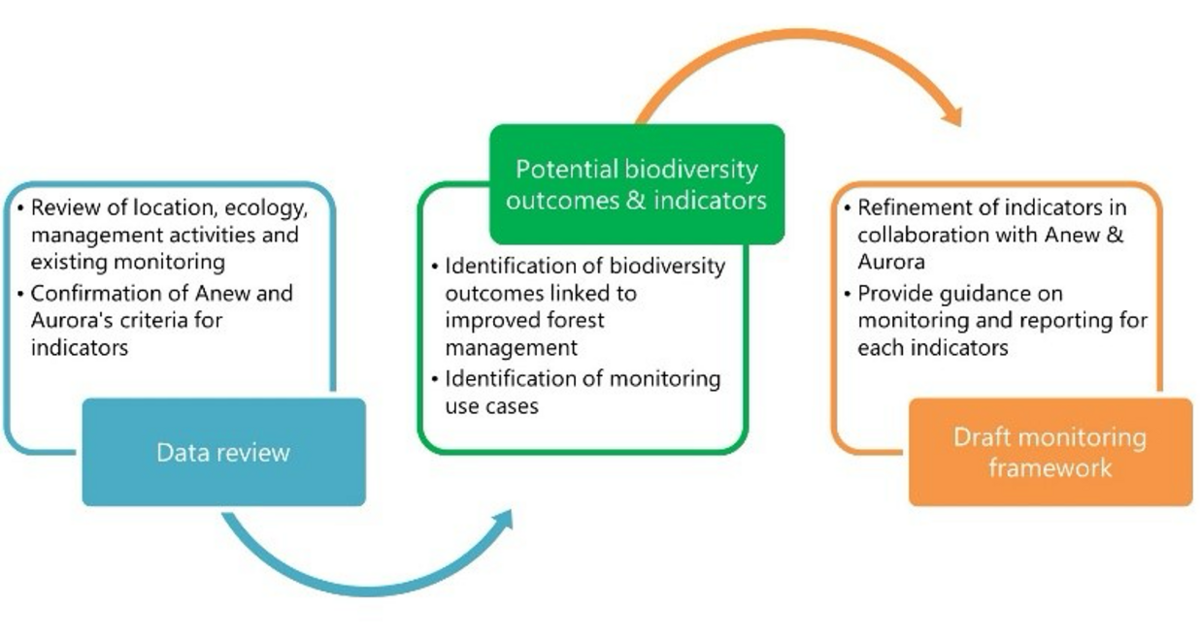
The Biodiversity Consultancy implemented a three-stage approach to develop a tailored monitoring framework:
1. Data review
TBC reviewed the literature on forestry monitoring and indicators, alongside data provided by Aurora on the management activities and biogeography of its sites. The work focused on 28 sites currently managed by Aurora, located across the Eastern United States. The review unpacked the variety of ecologies, geographies and management actions that exist in Aurora’s portfolio and built an understanding of the variables influencing monitoring design across the focal sites.
2. Potential biodiversity outcomes & indicators
TBC analysed the data to identify a comprehensive list of potential biodiversity outcomes linked to Aurora’s IFM activities and corresponding indicators to monitor these outcomes. A use-case approach to monitoring (grouping sites by common attributes influencing monitoring design) provided a cost-effective structure, allowing indicators, methods (including baselining requirements) to be determined.
3. Draft monitoring framework
Drawing on our in-house expertise in forestry monitoring and biodiversity metrics, we developed a refined list of indicators based on Aurora’s criteria and requirements (e.g., in-house capacity, reporting needs). The final list represented different components of biodiversity, was tailored to forest ecosystems, and designed to detect positive outcomes from Aurora’s interventions. The framework provides a solid foundation for Aurora to build a defensible, cost-effective biodiversity monitoring program, capable of quantifying and communicating the impact of the company’s interventions on biodiversity.
Outcome – A science-based Monitoring Framework linked to Improved Forest Management (IFM)
To support Aurora in assessing the biodiversity impact of its forest management, we developed a practical, science-driven monitoring framework. It tracks intervention outcomes, informs nature-based climate strategies, and advances broader sustainability goals through three key components:
1. Recommended indicators and methods
A suite of practical, science-based indicators tailored to detect biodiversity changes linked to IFM. This suite of indicators recommended to Aurora is intended to be defensible (clear and evidenced links to IFM) and cost effective (capable of utilising remote sensing and other cost-effective monitoring technologies), while covering different components of biodiversity: structure, composition, significance.
2. Site-specific monitoring use cases
Fifteen distinct monitoring use cases spanning multiple bio-geographies were identified, guiding the selection of relevant biodiversity indicators and baseline conditions. Grouping sites by use case strengthens the framework by:
- Identifying biodiversity indicators suited to local conditions
- Defining suitable baseline/reference conditions for common indicators
3. Supporting guidance for implementation
Practical advice was provided on a range of key topics—including establishing baselines, sampling methods, and indicator species— to help guide implementation and alignment with Aurora's operational processes.
The framework equips Aurora with a robust and cost-effective structure for biodiversity monitoring with potential to enhance credibility, support reporting, facilitate adaptive management, strengthen market competitiveness, and align with key frameworks, such as TNFD (Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures). All of which enable Aurora to better communicate the biodiversity value of baseline site conditions, the benefits of its forest management interventions and the co-benefit quality of its carbon credits to stakeholders and the market.
